6 Foods That Cause Migraine
Millions of individuals worldwide suffer from migraine, a complicated neurological disorder that involves more than just a headache. Often misunderstood and underestimated, migraines can be debilitating and significantly impact a person’s quality of life.
In this blog, we’ll delve into the intricacies of migraines, exploring their symptoms, causes, foods that cause migraine, and potential treatments.
What Is A Migraine?

Migraine is a type of headache disorder characterized by recurrent, throbbing headaches typically affecting one side of the head. These headaches are often accompanied by other symptoms, such as nausea, vomiting, sensitivity to light and sound, and visual disturbances. Migraines can last for hours to days, and the severity of the pain can be incapacitating.
Here are the key characteristics of migraines:
- Headache
- Aura
- Triggers
- Phases
- Other Symptoms include nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light(Photophobia) and sound(Phonophobia).
What Causes Migraine?
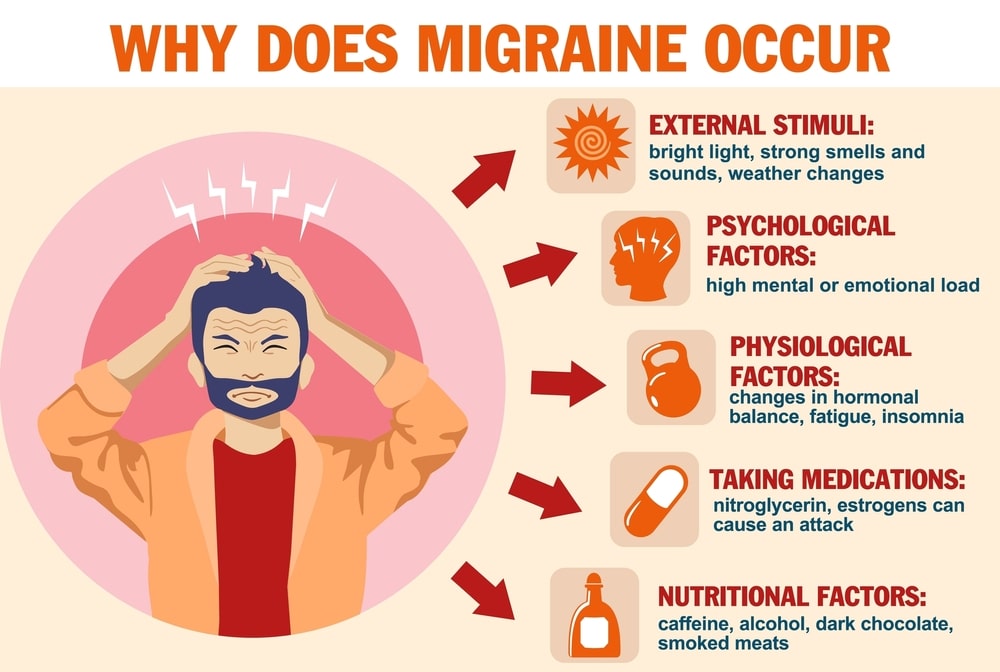
The multifaceted factors that contribute to the onset of migraines.
- Genetic Predisposition: One of the key contributors to migraines is genetic predisposition. Studies have shown that individuals with a family history of migraines are more likely to experience them themselves.
- Neurological Factors: The neurological aspect of migraines involves abnormal brain activity.
- Hormonal Fluctuations: Hormonal changes, particularly in women, play a significant role in triggering migraines.
- Triggers and Environmental Factors: Migraine triggers vary widely among individuals, but certain environmental factors consistently emerge as potential catalysts. These include Stress, Sensory Stimuli, Dietary Factors(Certain foods and drinks, such as chocolate, and caffeine), Sleep Patterns, and Irregular sleep patterns.
- Weather Changes: Some individuals report migraines triggered by changes in weather patterns, such as fluctuations in barometric pressure or extreme heat. While the exact mechanisms are not fully understood, environmental changes may influence the development of migraines in susceptible individuals.
Foods That Cause Migraine:

For individuals prone to migraines, the journey to identify and manage triggers often involves scrutinizing their diet. Certain foods have been identified as potential culprits in triggering migraines, and understanding these dietary triggers can be a crucial step in minimizing the frequency and intensity of these debilitating headaches. In this part, we’ll explore foods that cause migraine.
Tyramine-Rich Foods:
Tyramine, a naturally occurring compound, is found in various foods and can trigger migraines in susceptible individuals, making the top in the charts of foods that cause migraine.
Foods high in tyramine include:
- Aged cheeses(cheddar, gouda, and parmesan).
- Processed meats(sausages, pepperoni, and cured meats).
- Fermented foods(soy sauce, miso, and certain pickled items).
- Some alcoholic beverages(red wine and beer).
Caffeine:
While caffeine can offer relief for some migraine sufferers, it can also be a trigger for others. Abrupt changes in caffeine intake, whether an excess or withdrawal, may lead to migraines.
It’s essential to monitor and regulate caffeine consumption, considering not only coffee and tea but also energy drinks, chocolate, and some medications.
Aspartame and Artificial Sweeteners:
Aspartame, a common artificial sweetener, has been linked to migraines in some individuals. Diet sodas, sugar-free gum, and certain processed foods may contain aspartame, so those prone to migraines may want to limit their intake of these products.
Chocolate:
While the link between chocolate and migraines is not fully understood, some individuals report that chocolate can trigger or exacerbate their headaches. Chocolate contains caffeine and other compounds that may contribute to migraines in susceptible individuals.
MSG(Monosodium Glutamate):
MSG, a flavor enhancer commonly found in Chinese food, processed snacks, and some restaurant dishes, has been associated with migraines in some studies. While the evidence is not conclusive, individuals sensitive to MSG may experience headaches as a result of its consumption. This is one of the reasons for migraine and hence, qualifies to the list of foods that cause migraine.
Alcohol:
Alcohol, particularly red wine, beer, and certain spirits, is a well-known trigger for migraines. The exact mechanisms are not fully understood, but alcohol can lead to dehydration and changes in blood flow, both of which may contribute to migraines.
How To Get Rid Of A Migraine?
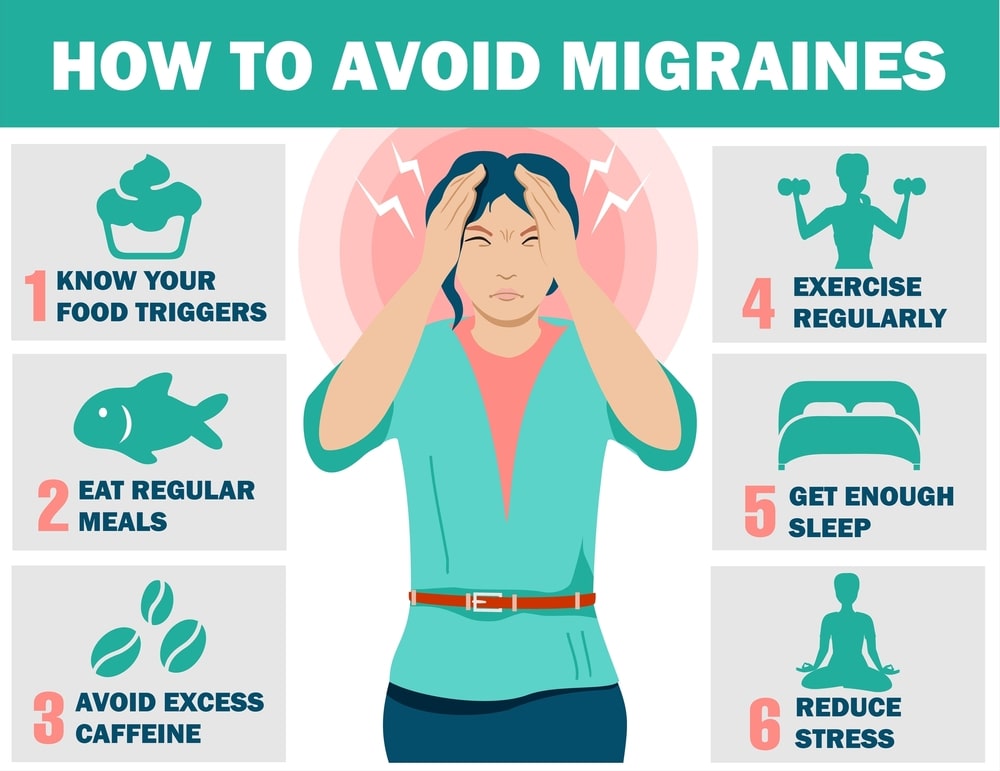
Here are some general tips:
- Rest in a Dark and Quiet Room: Find a calm and dark environment to rest in. Sensitivity to light and noise is common during migraines.
- Apply Cold or Warm Compresses: Placing a cold or warm compress on your forehead or neck may help ease the pain. Experiment with both to see which works best for you.
- Stay Hydrated: Dehydration can be a trigger for some people. Drink plenty of water throughout the day, especially if you notice the onset of a migraine.
- Manage Stress: Practice relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or yoga to help reduce stress, a common migraine trigger.
- Consider Caffeine: In some cases, caffeine can help relieve migraine symptoms. However, excessive caffeine intake or sudden withdrawal can also trigger migraines and make it a double-edged sword in the list of foods that cause migraines. So be mindful of your caffeine consumption.
- Get Adequate Sleep: Maintain a regular sleep schedule and ensure you get enough rest. Poor sleep habits can contribute to migraines.
- Acupuncture and Massage: Some individuals find relief from migraines through alternative therapies such as acupuncture or massage. These approaches focus on promoting relaxation and reducing tension.
- Migraine Medicines: Migraine medicines can be broadly categorized into two types: Acute(Abortive) medications and Preventive(Prophylactic) medications. The choice of medication depends on the frequency, severity, and specific characteristics of the migraines a person experiences. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable treatment plan. Here’s an overview of common migraine medications: such as Triptan, Naproxen, and Ibuprofen.
Endnote:
Identifying and managing dietary triggers is a crucial aspect of migraine management. While these foods may be associated with migraines in some individuals, it’s important to recognize that triggers can vary from person to person.
Keeping a detailed food diary, practicing moderation, and consulting with healthcare professionals can help individuals pinpoint their specific triggers and develop personalized strategies for managing migraines.
By understanding the connection between certain foods and migraines, foods that cause migraine, individuals can take proactive steps to minimize their impact on their overall well-being.
FAQs:
How long do migraines last?
An untreated migraine often lasts four to seventy-two hours. Each has migraines at different frequencies. A migraine may happen infrequently or multiple times per month.
Are migraines hereditary?
Migraine is largely influenced by genetics. It is therefore frequently inherited in families. It is thought that genetics account for as much as 60% of migraine cases. People with these genes are more susceptible to environmental changes, including lifestyle variables and triggers that may precipitate an attack.
Is migraine dangerous?
Although they rarely pose a threat, migraines significantly impair your quality of life. They also raise your chance of developing potentially fatal illnesses including heart attacks and strokes.
Can migraines cause fever?
Yes, migraines can cause fever due to extreme pain followed by fever.
What triggers migraines?
The triggering factors can range from medications, excessive coffee intake, alcohol consumption—especially red wine—and stress. Moreover, Sensory stimulation is brought on by potent scents or bright sights. There is a whole list of foods that cause migraine and it should be well understood and read.
References:
- https://www.ninds.nih.gov/health-information/disorders/migraine
- https://www.migrainedisorders.org/migraine-disorders/migraine-triggers/
- https://migrainetrust.org/understand-migraine/genetics-and-migraine/
- https://www.everydayhealth.com/headache-pictures/8-foods-that-trigger-headaches.aspx

