Early Diagnosis and Treatment of Arthritis will help in Immediate Recovery
A form of joint disorder, arthritis causes inflammation and stiffness in the joints. In this condition, a person experiences pain and swelling in the joints. It can affect people of all ages, sexes, and races; however, arthritis is most common among women. Although there’s no cure for arthritis, treatment of arthritis has improved greatly in recent years and, there’s a clear benefit in starting treatment at an early stage.
Today, arthritis is a major cause of disability in the United States. More than 50 million adults and 300,000 children suffer from some of the other types of arthritis. The most common symptoms of arthritis include pain, swelling of the joints, stiffness, and restricted physical movement. These symptoms can be mild, moderate, or severe, and may progress or get worse with time.
In severe cases, one may experience chronic pain, difficulty in walking or climbing stairs, and inability to do daily chores. The joint can also change permanently leading to knobby fingers. However, often joint damage can only be evident on an x-ray. Out of the different types of arthritis, some may also affect the eyes, heart, lungs, kidneys, and skin, along with the joints.
Different Types of Arthritis:
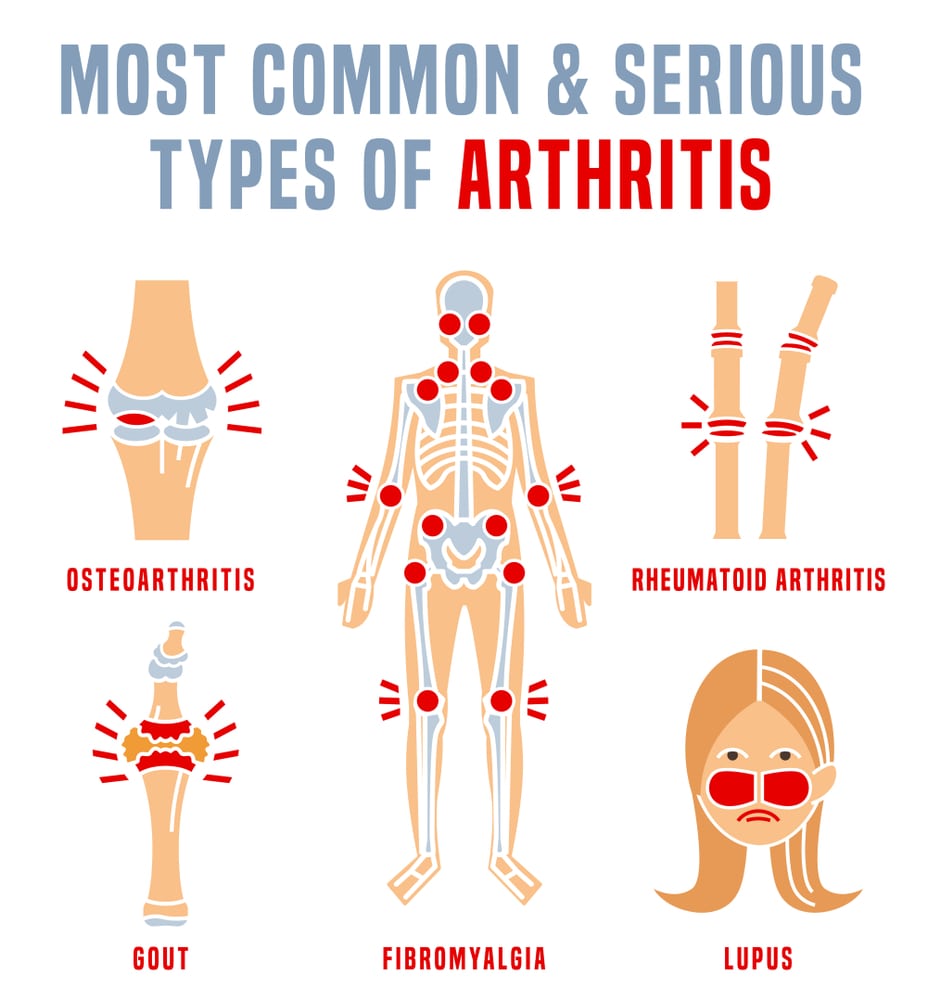
- Degenerative Arthritis: This type of arthritis is called Osteoarthritis and is the most common form. In this, the cartilage between the bones wears away which leads to bone rubbing against the bone. This causes pain, stiffness, and swelling. One may get affected due to excess weight, age, family history, or previous injury.
- Inflammatory Arthritis: Psoriatic and Rheumatoid arthritis are examples of inflammatory arthritis. In this case, the body’s immune system gets confused and attacks the healthy joints leading to inflammation, pain, stiffness, and sometimes swelling and redness. Genetics and environmental aspects may trigger autoimmunity, according to researchers.
- Infectious Arthritis: In this case, a virus, fungus, or bacterium enters the joint, triggering inflammation. A suitable treatment, along with antibiotics, may treat the infection before it turns chronic.
- Metabolic Arthritis: High levels of uric acid lead to this kind of arthritis. The uric acid levels increase and form needle-like crystals in the joints which leads to extreme joint pain or a gout attack.
Arthritis Diagnosis And Laboratory Tests:
During the physical assessment, healthcare providers check a person’s joints for inflammation, warmth, and redness. Also, they wish to identify how well the movement of the joints is and how well the treatment of arthritis will work.
The examination of various types of body fluids may aid in determining the type of arthritis a person might experience. Fluids commonly assessed may involve urine, blood, and joint fluid. To find a joint fluid sample, healthcare providers wash and numb the area before introducing a needle into the joint space to remove some fluid.
A healthcare provider might carry out a physical assessment. Also, diagnosis of arthritis can be performed using blood tests and image scans. Furthermore, to identify the severity of the condition a healthcare provider might ask the patient to go for an ultrasound, CT scan, or X-ray.
Even if there is no single treatment for arthritis, in various cases, the damage and condition may be effectively controlled using early diagnosis and treatment.
Here are some of the tests for Arthritis:
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): It combines radio waves with a strong magnetic field. The test also produces thorough cross-sectional images of soft tissues like tendons, cartilages, and ligaments.
- X-rays: They make use of low levels of radiation to visualize bone. Also, X-rays identify bone damage, cartilage loss, and bone outgrowths. X-rays might not locate primary arthritic damage; however, they often can be utilized to track the development of problems.
- Ultrasound: This technology makes use of high-frequency sound waves. It produces images of cartilages, soft tissues, and fluid-containing structures present close to the joints (bursae). Moreover, ultrasound guides the needle location for taking away joint fluid or injecting drugs into the joint.
- Computerized tomography (CT): This test takes X-rays from several different angles and combines the data to produce cross-sectional images of inner structures. Also, CTs may help to visualize bone and the adjacent soft tissues.
Arthritis Treatment:
Researchers strongly believe in the early treatment of arthritis through aggressive regimes of drugs and physical therapies. In the case of inflammatory arthritis, early drug therapies help in reducing the risk of long-term damage to joints and bones. Certain hydrotherapy, physiotherapy, and occupational therapy also help ease the pain.
If the joints are severely damaged then one may have to undergo surgery such as joint replacements. All scientific and medical societies worldwide insist on early and aggressive treatment of arthritis to stop the progression of damage to joints and halt symptoms. Arthritis treatment concentrates on mitigating the signs and improving joint function.
Arthritis Medicines:
The medicines for the treatment of arthritis may differ based on the type of arthritis. Commonly used arthritis drugs are:
- Counterirritants: A few ranges of ointments and creams comprise menthol or capsaicin. It is a constituent that increases the spiciness of hot peppers. Rubbing such formulations over the skin during pain might slow the spread of pain signals from the joint.
- Steroids: Corticosteroid drugs including prednisone help to lower pain and swelling. Also, these medications slow joint damage. These drugs are available as a pill or as an injection into the aching joint. Side effects are weight gain, high blood sugar, and thinning of bones.
- NSAIDs: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as Aspirin help to decrease pain and inflammation. These drugs include ibuprofen and naproxen sodium. Stronger NSAIDs may result in stomach irritation and might enhance the risk of heart attack or stroke. These drugs are available in the form of gels or creams.
- Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs): These medications decrease the development of rheumatoid arthritis. Also, they save the joints or other tissues from lasting damage. Side effects may differ, however many DMARDs augment the risk of infections.
Therapy:
Physical therapy might be useful for varied types of arthritis. Exercise may help to improve the range of motion. Also, they help to reinforce the muscles surrounding joints. In a few cases, splints or braces may be necessary.
Surgery:
If conservative measures fail to work, healthcare providers might recommend surgery, including:
- Joint Replacement: This process removes the damaged joint and substitutes it with an artificial one. The most common replacement of the joints is the hips and knees.
- Joint Repair: In a few instances, smoothening or realignment of the joint surfaces can be done. This helps to decrease the pain and improve function. These kinds of treatment of arthritis may be carried out arthroscopically. In other words, via small incisions over the joint.
- Joint Fusion: This process is more useful for smaller joints, like those in the ankle, wrist, and fingers. It takes away the ends of the two bones in the joint.
Arthritis Diet:
No particular diet cures arthritis; however, a few kinds of food might aid in decreasing inflammation. The following foods, present in a Mediterranean diet, might offer several nutrients important for joint health:
- Nuts and seeds
- Fruits and veggies
- Whole grains
- Beans
- Fish
- Olive oil
Foods to avoid:
There are a few foods that individuals experiencing arthritis must avoid. Nightshade veggies including tomatoes comprise a chemical named solanine that a few studies have associated with arthritis pain.
Self-management:
Self-care of arthritis signs is also vital. Key approaches may include:
- Attaining and maintaining a healthy weight.
- Staying physically active.
- Getting consistent check-ups with the concerned healthcare provider.
- Shielding the joints from unwanted stress.
Some habits that may aid an individual with arthritis to manage their condition include:
- Consumption of a healthy diet: A well-balanced diet helps attain a healthy weight and control inflammation. People must not have refined, processed foods and pro-inflammatory animal products. Also, they must opt for whole plant foods rich in antioxidants and contain anti-inflammatory properties.
- Management of pain and fatigue: In this, a combination of a medication regimen and non-medical pain management is given. People must learn to manage fatigue to live comfortably with arthritis.
- Staying physically active: Exercise helps manage overall health.
- Being organized: Follow signs, pain levels, medicines, and possible side effects for regular check-ups with a doctor.
- Balancing exercises with rest: On top of staying physically active, rest is equally vital when the health problem is active.
- Improving Sleep: Poor sleep may worsen arthritis pain and fatigue. People must take steps to improve their sleep hygiene. They must not have caffeine and avoid strenuous exercise in the evenings. Also, they must limit their screen time before sleeping.
- Caring for Joints: People must utilize the stronger, larger joints as levers while opening doors, making use of numerous joints to spread the weight of an object including the usage of a backpack and gripping loosely by utilizing padded handles.
With early diagnosis, managing a majority of forms of arthritis is important. Also, the pain and disability can be reduced. Moreover, early diagnosis and treatment of arthritis might be capable of avoiding tissue damage due to arthritis. Early, aggressive treatment is chiefly significant for arthritis. This helps to prevent additional damage and incapacity.

