How Does Sleep Affect Your Health?
In our hectic, contemporary lifestyles, sleep frequently suffers as a result of our numerous responsibilities and workload. However, the importance of getting a good night’s sleep cannot be emphasized. There is a strong correlation between sleep and health, as it affects both our mental and physical health.
There are actual long-term consequences to sleep deprivation. When sleep deprivation starts affecting our day-to-day life people hunt to know how does sleep affect your health. To bring an end to such queries we have tried summarising a few answers “How does sleep affect your health?” in this article.
How does sleep affect mental health?

While trying to get an answer for how does sleep affect your health let us explore its segment-wise of complete body.
Sleep affects whole body functions. Let us understand more about how does sleep affect mental health. Sleep is essential for healthy brain function. Your brain is preparing for the next day as you sleep. It is creating new neural connections to support information learning and retention.
Research indicates that getting enough sleep enhances one’s ability for cognitive processes including learning, problem-solving, and memory consolidation. It facilitates the processing and archiving of data that is gathered throughout the day. Moreover, sleep promotes creativity, decision-making, and attention spans.
Getting enough sleep helps people manage their emotions and be emotionally resilient. An increased risk of mood disorders, anxiety, and sadness has been associated with sleep deprivation. A natural stress-regulatory mechanism is sleep. A well-rested mind fosters emotional and mental resilience and is better able to manage everyday challenges.
Research indicates that insufficient sleep alters the functioning of specific brain regions. Lack of sleep can affect your ability to make decisions, solve issues, regulate your emotions and behavior, and adjust to change. Lack of sleep has also been connected to suicidal thoughts, sadness, and reckless behavior.
Teens and kids who don’t get enough sleep may find it difficult to get along with other people. They might experience mood fluctuations, feel agitated and impetuous, melancholy or despondent, or lack motivation. They might also struggle to focus, receive worse marks, and experience stress.
Extended sleep deprivation affects decision-making, attention, and cognitive function. It impairs performance in day-to-day activities by simulating the symptoms of alcohol intoxication.
How does sleep affect physical health?
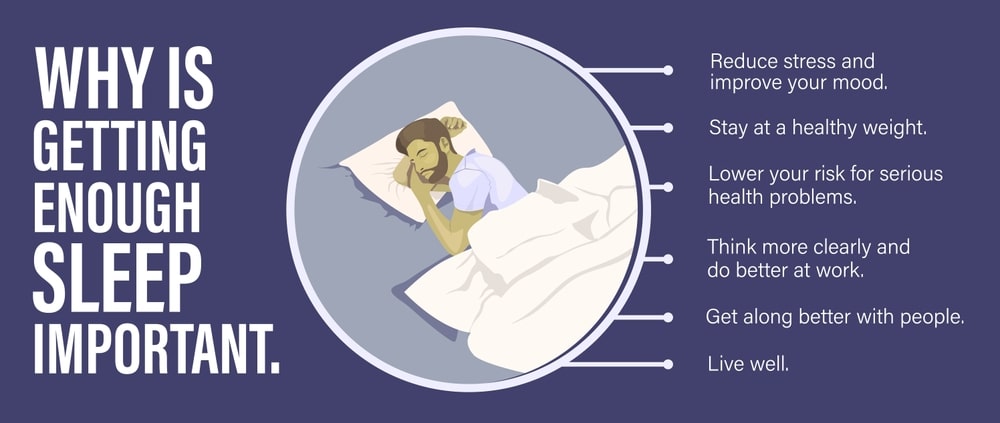
After seeking the correlation between sleep and mental health, to seek more clarity on how does sleep affect your health, we will discuss physical health.
Sleep not only affects our mental health. It also affects our physical health. Let us know more about how does sleep affect physical health. Chronic sleep deprivation is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, including hypertension and heart attacks.
Sleep deprivation may knock off the hormones that control appetite, which can result in weight gain, insulin resistance, and a higher chance of Type 2 Diabetes.
Your immune system creates antibodies and cytokines, which are molecules that fight infections, while you sleep. It uses these materials to fight off alien invaders like viruses and bacteria. Additionally, some cytokines promote better sleep, which boosts the effectiveness of your immune system in protecting your body from disease.
Lack of sleep inhibits the immune system’s ability to strengthen itself. Your body may not be able to fight off intruders and recovery from disease may take longer if you don’t get enough sleep.
There is a reciprocal interaction between the respiratory system and sleep. Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a breathing disorder that affects people during the night. It can cause sleep disturbances and poor-quality sleep.
This can lead to sleep deprivation as you wake up during the night, making you more susceptible to respiratory illnesses like the flu and the common cold. Lack of sleep can exacerbate pre-existing respiratory conditions such as chronic lung sickness.
How does sleep affect your health?

In a nutshell, persistently getting too little sleep or sleep of poor quality is the root cause of sleep deprivation. Regularly getting less than 7 hours of sleep can eventually hurt your overall body’s health. A sleep issue that is underlying may be the cause of this.
To perform at its optimum, your body requires food, air, and sleep. Your body repairs itself and rebalances its chemicals as you sleep. Your brain aids in memory retention and creates new connections between ideas. Your body’s processes, including your brain, malfunction if you don’t get enough sleep. It can also significantly impair your standard of living.
What happens during your sleep has an impact on how you feel during the day. Your body is attempting to maintain both your physical and mental health while you sleep. Sleep is also important for promoting growth and development in kids and teenagers.
Sleep deprivation can cause long-term harm or instantaneous damage, like in a car accident. For instance, persistent sleep deprivation can increase your risk of developing some long-term health issues. It also has an impact on your ability to think, behave, learn, work, and get along with people.
What are the three physical benefits of quality sleep?
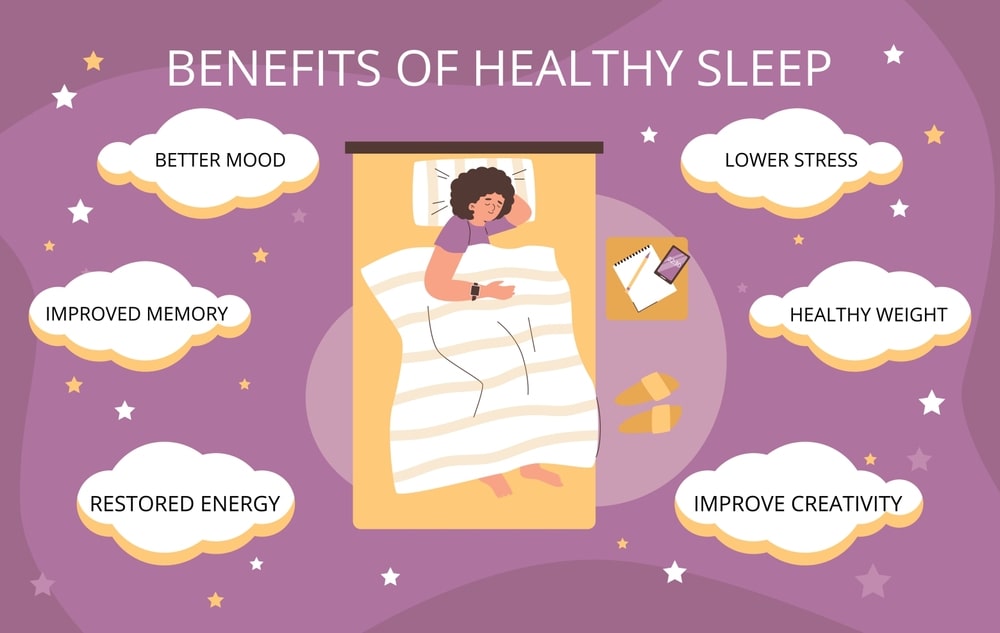
Here are three key physical benefits associated with getting sufficient, high-quality sleep:
- Enhanced Growth and Repair of Cells: The body performs necessary maintenance and repair tasks during deep sleep stages. Cellular growth processes are optimized, and muscles and tissues are restored. Deep sleep is when growth hormone is released at its highest, which aids in the mending of bones, tissues, and cells. This is essential for general physical development and healing.
- Enhanced Immune Response: Strong immunity is intimately associated with getting enough good sleep. Enough sleep promotes the creation of proteins, including cytokines, and immune cells. While the body is sleeping, the immune system works more efficiently to protect the body from infections, viruses, and other pathogens. Chronic sleep deprivation has been linked to immune system deterioration, increasing disease susceptibility.
- Balanced Hormone Control: Sleep is essential for preserving hormonal balance since it affects several different hormones that control body processes. The stress hormone cortisol has a natural circadian cycle; it peaks early in the morning and troughs deep sleep at its lowest levels. This aids in the appropriate handling and reaction to stress. Sleep has an impact on insulin sensitivity, which is crucial for blood sugar management and metabolism. A lack of sleep can increase insulin resistance, which raises the risk of metabolic diseases.
Tips for a healthy sleep:

After seeking information on how does sleep affect your health next comes how to get healthy sleep. Below are some of the healthy tips for a healthy sleep:
- Maintain a Consistent Sleep Schedule: Even on the weekends, go to bed and wake up at the same time every day. This aids in the internal clock regulation of your body.
- Establish a warm cosy Sleep Environment: Keep your bedroom calm, dark, and cold to create a sleeping environment.
- Minimise Screen Time Before Bed: Limit your time spent using phones, tablets, and computers that have screens at least one hour before bed. The generation of melatonin, the hormone that promotes sleep, may be disrupted by the emission of blue light.
- Create a Calm Before Bedtime Routine: Before bed, engage in relaxing activities like reading a book, having a warm bath, or other relaxation techniques. Your body will receive this as an indicator for you to wind down.
- Keep an eye on your diet: Stay away from large meals, coffee, and nicotine close to bedtime as they can cause sleep disturbances. Before going to bed, if you’re hungry, choose a small snack.
- Exercise Regularly: Frequent exercise can help you sleep better. Try to get in at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week; however, stay away from long, strenuous activities right before bed.
- Handle Stress: To relax before going to bed, try stress-reduction methods like deep breathing, meditation, or mindfulness.
- Limit Day Naps: Try not to take naps too close to bedtime and limit them to no more than 20 to 30 minutes during the day if you even consider taking a short nap during the daytime.
- Treat Sleep Disorders: For an accurate diagnosis and course of therapy, speak with a medical expert if you believe you may have a sleep condition, such as insomnia or sleep apnea.
- Steer clear of clock watching: Checking the time all the time might lead to worry and make it more difficult to get back to sleep if you wake up in the middle of the night. Think about moving the clock out of your direct line of sight.
FAQs:
Is sleeping naked good for health?
Some people can better control their body’s temperature while they sleep unclothed. You may improve air circulation and let your skin breathe by going to bed without clothes on. Many people discover that sleeping without clothes improves their comfort and permits them to sleep more soundly and peacefully. Sleeping unclothed may aid in the regulation of the stress hormone cortisol and the hormone that controls sleep, Melatonin.
How does lack of sleep affect mental health?
Talking about how does sleep affect your health, mental health counts the most these days. Sleep deprivation has a profound effect on mental health, causing problems including poor concentration, mood swings, worry, and tension, as well as an increased chance of mood disorders like depression.
How does sleep affect your heart health?
Getting enough good sleep is essential for heart health. A higher risk of cardiovascular problems, such as hypertension, heart disease, and stroke, may result from inadequate sleep. Heart health is influenced by blood pressure, inflammation, and stress hormones, all of which are regulated by sleep.
How does sleeping on your left side affect your health?
Sleeping on your left side can ease organ pressure, improve lymphatic drainage, reduce acid reflux, and improve digestion. It can be particularly comfortable for expecting mothers and has potential heart health benefits. The most comfortable position for each person and their unique health circumstances should be considered.
Why is quality sleep important for mental and physical health?
While seeking an answer on how does sleep affect your health both physical health and mental health are pivotal along with quality sleep. Since it promotes cognitive performance, emotional stability, and physical healing, getting enough sound sleep is essential for both mental and physical health. It supports immune system function, aids in hormone regulation, and promotes general vigor and resilience.
References:
- https://www.healthline.com/health/sleep-deprivation/effects-on-body#Treatment-for-sleep-deprivation
- https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/sleep-deprivation/health-effects
- https://www.reidhealth.org/blog/7-ways-lack-of-sleep-can-impact-your-health

