How To Stop Drinking Alcohol?
Alcohol has addictive assets and is a harmful, psychoactive drug. Alcoholic beverages are often consumed by a large portion of the population in many modern civilizations. If you routinely drink and have more than one or two drinks when you do, these effects can be more severe and obvious. There comes the need for a handy guide on how to stop drinking.

This is especially true for people who frequent highly visible, globally influential social settings where drinking often goes hand in hand with socializing. Over time, alcohol usage can start to negatively impact anyone’s physical and mental health.
Although you might not instantly feel the effects of alcohol on your body, they instigate as soon as you take your first sip. If you drink, you’ve certainly experienced some of the effects of alcohol, from the warm rush that starts to wear off swiftly to the unpleasant wine headache or the hangover that appears the next day. You might not be really concerned about them because they don’t last long, especially if you don’t drink frequently.
Worldwide, drinking alcohol contributes to 3 million fatalities each year, as well as millions of impairments and ill health. Let’s understand more in details about how to stop drinking alcohol.
What happens when you Stop drinking Alcohol?
- What happens when you Stop drinking Alcohol?
- Short Term Effects of Alcohol:
- Long Term Effects of Alcohol:
- The Physical Consequences of Alcohol on the Body:
- Benefits of not drinking alcohol:
- Tips to Stop Drinking Alcohol:
- Benefits to Stop Drinking Alcohol:
- Medications to Stop Drinking Alcohol:
- Effect of Alcohol on the Brain:
- Take Home Message:
- FAQs:
The beginning of withdrawal symptoms may include shaking hands, vomiting, profuse clammy, restlessness, and anxiety. Continued withdrawal symptoms, Cravings for alcohol, low energy, and feeling down or melancholy are all typical. Sleep disturbances are likely. So, it is essential to know how to stop drinking alcohol.
Short Term Effects of Alcohol:

The temporary effect, a person might notice while drinking alcohol (or shortly after) can include:
- Feelings of relaxation or drowsiness
- A sense of euphoria or giddiness
- Changes in mood
- Lowered inhibitions
- Impulsive behavior
- Slowed or slurred speech
- Nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Head pain
- Changes in hearing, vision, and perception
- Loss of coordination
- Trouble focusing or making decisions
- Loss of consciousness or gaps in memory (often called a blackout)
Long Term Effects of Alcohol:
Alcohol use can also lead to more lasting concerns that extend yonder your own mood and health.
Some long-term effects of frequently drinking alcohol can include:
- Persistent changes in mood, including anxiety and irritability
- Insomnia and other sleep concerns
- A weakened immune system, alcohol can actually diminish our body’s natural defenses
- Changes in libido and sexual function
- Changes in appetite and weight, heavy alcohol consumption was a huge contributor to abdominal obesity.
- Problems with memory and concentration
- Difficulty focusing on tasks
- Increased tension and conflict in romantic and family relationships.

Alcohol has been allied with 7 malignancies, including three different types of throat cancer, liver cancer, bowel cancer, and mouth cancer. Alcohol can decompose into the acetaldehyde molecule, which alters our cells and can lead to the growth of malignant tumors. Brain cells are destroyed by alcohol. It suppresses chemical communication between brain cells (called neurons).
You may start to feel psychological symptoms like depression, anxiety, or agitation as your body processes alcohol. Alcohol can impair our brain’s capacity to work properly, slowing down speech, memory, and motor skills. Immoderation in alcohol over an extended period of time can cause brain damage and may raise your risk of dementia.
The Physical Consequences of Alcohol on the Body:
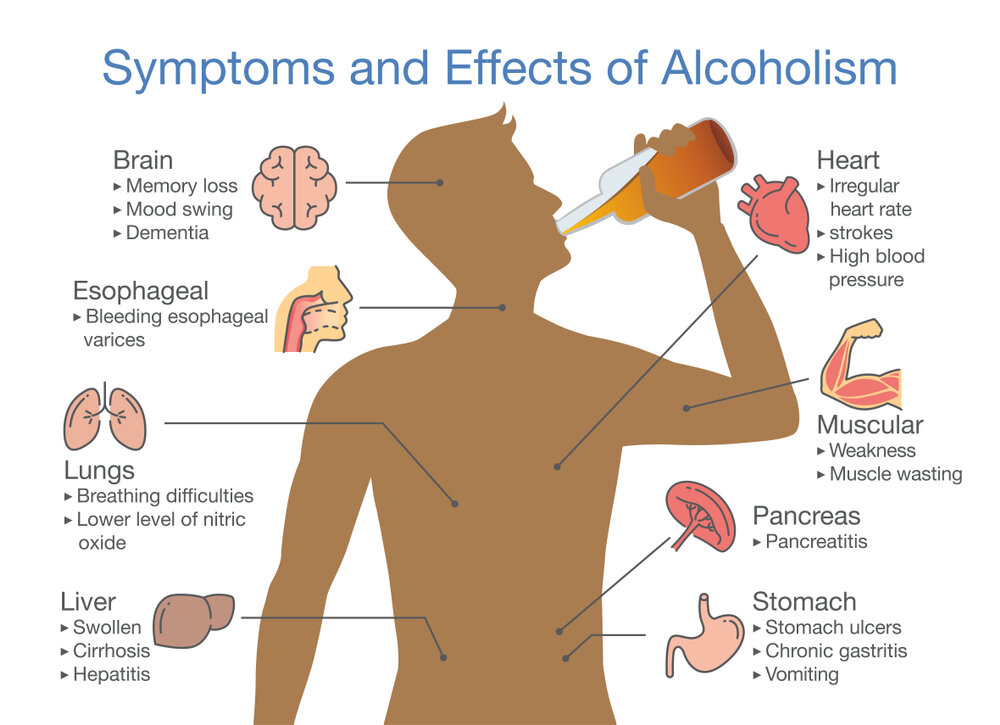
The Effects of Alcohol on your Internal Organs and Bodily Functions are Listed here.
Endocrine and Digestive Glands:
Over time, excessive alcohol consumption may upshot in pancreas inflammation and pancreatitis. Abdominal pain and digestive enzyme release can both be brought on by pancreatitis. Serious consequences and a long-term disease can result from pancreatitis. So, it is essential to know how to stop drinking alcohol.
An Inflammatory Injury:

Alcohol is one of the toxic chemicals that your liver aids in the breakdown and removal. Alcohol abuse for a long period of time impedes this process. Additionally, it raises your risk of developing chronic liver inflammation and liver disease brought on by alcohol:
Alcohol-related liver illness can be fatal and causes your body to accumulate waste and poisons. Chronic liver inflammation can result in scarring or cirrhosis. Your liver may suffer long-term harm from scar tissue. So, it is essential to know how to stop drinking alcohol.
Glucose Levels:
Your body’s response to glucose and the utilization of insulin are both regulated by the pancreas. You may have hypoglycemia or low blood sugar if your pancreas and liver aren’t functioning properly as a result of pancreatitis or liver illness. Additionally, a malfunctioning pancreas may limit the amount of insulin your body can produce and use to use sugar. Hyperglycemia, or having too much sugar in the blood, can result from this.
The consequences and side effects of diabetes may worsen if your body is unable to control and regulate your blood sugar levels. If you have diabetes or hypoglycemia, experts advise staying away from heavy alcohol use. So, it is essential to know how to stop drinking alcohol.
Central Nervous System:

One key indicator of how alcohol affects your body is? Recognizing the impact on your central nervous system. Alcohol impairs brain-body communication, which effects in slurred speech, a crucial indicator of intoxication. Speech and coordination become more challenging as a result (consider response time and balance). That is a key factor in the advice to never drive after drinking.
Alcohol can harm your central nervous system over time. Your hands and feet may start to feel tingly and numb.
Drinking can also affect your ability to:
- Create long-term memories
- Think clearly
- Make rational choices
- Regulate your emotions
Drinking over time can also harm your frontal lobe, which is the area of the brain in charge of decision-making processes like abstract thought, judgment, social behavior, and performance. Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome, a memory-related brain condition, is one of the lifelong brain injuries that can result from chronic excessive drinking.
Digestive System:
Drinking can harm the tissues in your digestive tract, making it difficult for your intestines to properly digest food and assimilate vitamins and nutrients. Malnutrition may result from this harm over time. The link between drinking alcohol and digestive health may not be immediately obvious. Often, the adverse effects don’t show up until later, The damage has been done. Drinking more can make these symptoms worse. So, it is essential to know how to stop drinking alcohol.
Heavy drinking can also lead to:
- Gas
- Bloating
- Feeling of fullness in your abdomen
- Diarrhea or painful stools
- Ulcers or hemorrhoids (due to dehydration and constipation)
Ulcers can cause dangerous internal bleeding, which can sometimes be fatal without prompt diagnosis and treatment.
Circulatory System:

Chronic drinking can affect your heart and lungs, raising your risk of developing heart-related health issues.
Circulatory system complications include:
- High blood pressure
- Irregular heartbeat
- Difficulty pumping blood through the body
- Stroke
- Heart attack
- Heart disease
- Heart failure
Sexual and Reproductive Health:

You might imagine that since alcohol can lessen inhibitions, it will increase the amount of enjoyment you have in bed.
In reality, though, heavy drinking can:
- Prevent Sex Hormone Production
- Lower your Libido
- Keep you from getting or maintaining an Erection
- Make it difficult to achieve Orgasm
Excessive drinking may affect your menstrual cycle and potentially increase your risk for infertility. So, it is essential to know how to stop drinking alcohol.
Skeletal and Muscle Systems:
Alcohol abuse over a long period of time can reduce bone density, making bones brittle and raising the possibility of fractures in the event of a fall. Bones that are weaker may also mend more slowly. Alcohol use can also cause cramping, atrophy, and muscle weakening. So, it is essential to know how to stop drinking alcohol.
Immune System:
The natural immune system of your body is compromised by heavy drinking. Your immune system works harder to defend you against viruses and bacteria when it is compromised. So, it is essential to know how to stop drinking alcohol.
Behavioral Effects:
Alcohol abuse over a Long period of time might alter your Brain in ways that include:
- Memory and concentration,
- Impulse control,
- Emotions, mood, and personality.
Regular drinking can have a adverse impact on one’s general mental health and wellbeing, in part because it can make the symptoms of some mental health problems, such as depression, anxiety, and bipolar disorder, worse. With a hangover, you could also experience sensations of worry. So, it is essential to know how to stop drinking alcohol.
Alcohol-induced mental health conditions:
When mental health symptoms closely mimic those of other mental health issues, alcohol consumption can contribute to such symptoms. Diagnostic criteria for the following are included in the most recent version of The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), which is used by mental health practitioners to identify mental health conditions:
- Alcohol-induced bipolar disorder
- Alcohol-induced psychotic disorder
- Alcohol-induced sleep disorder
- Alcohol-induced depressive disorder
- Alcohol-induced anxiety disorder
With these conditions, you’ll only notice symptoms during alcohol intoxication or withdrawal. These symptoms typically improve quickly when alcohol use stops. So, it is essential to know how to stop drinking alcohol.
Benefits of not drinking alcohol:
Alcohol withdrawal can be challenging and, in some instances, fatal. If you wish to stop drinking, you might need support from a healthcare provider depending on how much and how frequently you drink.
It is always prudent to speak with your doctor before stop drinking. Going “cold turkey” might not always be a good idea. If you’re trying to stop drinking, have these positive belief in mind:
- Improved cognition and problem-solving
- Increased mental focus and improved memory function
- Improved digestion and removal of harmful toxins
- Increased absorption of vitamins and minerals
- Weight loss due to less caloric intake
- Reduced sugar intake (as long as alcohol is not replaced with sugar-heavy foods)
- Reduced risk of heart disease and alcohol-related cancers
- Better immune system
- Improved heart function
Stopping drinking can be done at any time. Your intellect and the body may be tested during the procedure. But when done responsibly, giving-up alcohol can help you become a happier and healthier person. You can heal your body while avoiding the dangers of drinking. So, it is essential to know how to stop drinking alcohol.
Tips to Stop Drinking Alcohol:

- Find the appropriate strategy for your scenario and the easy way to stop drinking as you concentrate on minimizing alcohol usage and the possible damages that it brings.
- Avoid giving in to temptation. Avoid those who or things that make you desire to drink.
- Create an advanced strategy for handling events that you connect with drinking, such as holidays or vacations. Watch your emotions. The best tip to stop drinking.
- Forging new connections with those who refrain from drinking alcohol might be quite beneficial. It is better to have more support.
- Switching up your routine will help you break a pattern by keeping you occupied and diverting your attention from bad habits. The most beneficial activities are those that regularly get you outside and moving.
- Be tenacious: This tip to stop drinking helps most people to take multiple tries before effectively reducing their alcohol intake or quitting altogether. Setbacks are certain to occur, but don’t let them prevent you from achieving your long-term objective. Since the process typically necessitates continual work, there is actually no definitive endpoint.
- Declare what you intend to do. Inform your loved ones that you intend to stop consuming alcohol and give them an explanation.
Benefits to Stop Drinking Alcohol:
For some people, quitting drinking alcohol can first seem like a major life adjustment. Your chance of contracting a serious disease will be significantly decreased if you stop drinking alcohol altogether or significantly reduce how much you consume.
Reducing your usage can significantly improve your capacity for logical decision-making and enable your brain to operate normally and healthily. In fact, studies have shown that when people entirely stop drinking alcohol, their brains can recover from the harm it caused. Although it could take a few months to fully reap the benefits, giving up alcohol can help you control your mood.
Alcohol addiction recovery can be a challenging and drawn-out process. It might even seem impossible at times. Yet it isn’t. No matter how much you drink or how helpless you feel, if you’re ready to stop and prepared to obtain the help you need, you can beat alcoholism and alcohol abuse. Furthermore, you can change at any time; you don’t have to wait until you’ve reached your lowest point.
The majority of persons who struggle with alcoholism do not suddenly decide to change drastically or drastically alter their drinking patterns. Recovery typically happens over time. Denial is a significant barrier during the early phases of change. Even once you acknowledge that you have a drinking issue, you could still find reasons to put things off.
It’s critical to identify your conflicted feelings around quitting drinking. Consider the costs and benefits of each option if you’re unsure of your readiness for change or are having trouble making a decision. It is essential to know how to stop drinking alcohol.
Medications to Stop Drinking Alcohol:

Few individuals are aware of how to stop drinking alcohol and that there are drugs available to treat alcohol use disorder, also known as alcoholism and alcohol abuse. For alcohol use disorders, the FDA has approved three medications to stop drinking, each of which functions differently.
Disulfiram:
This was the first medication for stopping drinking and it is used as a disorder medicine that FDA licensed in 1951. Antabuse (Disulfiram) alters how your body breaks down alcohol. You get nauseous if you drink while taking it. And as a result, you’ll probably consume less alcohol.
Naltrexone:
When consuming alcohol while using Naltrexone, you may become inebriated but not experience the typical high that comes with it. You’re attempting to eliminate any benefits from your relationship with booze, says Holt. According to him, the medicine can also aid in preventing cravings. When you have an alcohol use disorder, your brain experiences pleasure at the mere thought of drinking. “Naltrexone may assist in separating alcohol from pleasure.”
Acamprosate:
Acamprosate (Campral) lessens withdrawal symptoms, which can persist for months after you quit drinking and include restlessness, anxiety, insomnia, and feeling down. Gamma-aminobutyric acid, or GABA, and glutamate are two chemical messengers that the brain uses to communicate. When GABA functions properly, it can help reduce the fear or anxiety you experience when particular nerve cells become overexcited.
On the other hand, glutamate activates nerve cells. Acamprosate is intended to stabilize the anomalies and level them out. The requirement to take two pills three times per day is one downside. Acamprosate, like naltrexone, tends to perform best for those who are able to give up drinking prior to beginning therapy.
Effect of Alcohol on the Brain:
Alcohol can change how the brain functions and looks by interfering with the brain’s communication networks. Alcohol impairs the function of the brain and it affects the brain and its regions in charge of balance, memory, speech, and judgment, increasing the risk of accidents and other unfavorable outcomes. So, it is essential to know how to stop drinking alcohol.
Take Home Message:
Giving off alcohol can take some time. If it first doesn’t stick, be kind to yourself. Whether your ultimate objective is total abstinence or just more moderate drinking, you’re still doing your body and brain a lot of good and following how to stop drinking can help you land somewhere better.
FAQs:
If I Stop Drinking Alcohol will my ED (Erectile dysfunction) go away?
There is plenty of data, nevertheless, to suggest that sexual dysfunction brought on by alcohol is, for the most part, curable by quitting drinking.
Will I Lose Weight if I Stop Drinking Alcohol?
Alcohol calories in excess can cause weight gain. People who regularly consume moderate to large amounts of alcohol can lose excess weight more readily. When you stop drinking alcohol, you could experience fewer desires for food.
Will ascites go away if I Stop Drinking Alcohol?
Avoiding smoking, exercising, eating less salt, and drinking no alcohol at all will help avoid cirrhosis or cancer that can cause ascites. Although ascites cannot be cured, lifestyle modifications and treatments may lessen problems.
What happens when alcoholics stop drinking?
The beginning of withdrawal symptoms may include shaking hands, vomiting, profuse perspiring, restlessness, and anxiety. Cravings for alcohol, low energy, and feeling down or melancholy are all typical. Sleep disturbances are likely.
How Long for Hormones to Balance after Stop Drinking Alcohol?
Initially two weeks after following how to stop drinking. The majority of people stop suffering withdrawal symptoms in less than a week, at which point their bodies start to operate normally again and their quality of life can already be noticeably better. Some sleep benefits start to happen as soon as seven days, and they continue to grow the following week.

