Psoriasis vs Eczema: Let’s Understand The Differences In 15 points
Psoriasis vs Eczema, both appear very similar to the untrained eye. The development of red, dry patches of skin can be itchy, embarrassing, and detrimental to the quality of life. Even though these two common skin illnesses have some similar traits and treatment options, their underlying causes are different, which affects the optimal strategy for preventing flare-ups in the future.
There are techniques to distinguish Psoriasis vs Eczema, the two skin disorders, even when they have similar symptoms.
Difference between Eczema and Psoriasis:
- Difference between Eczema and Psoriasis:
- Psoriasis vs Eczema on face:
- Psoriasis vs Eczema, Where they appear:
- Psoriasis vs Eczema, What are the triggering factors:
- Psoriasis vs Eczema, by what age do they begin?
- Psoriasis vs Eczema, Conditions They Are Related To:
- Psoriasis vs Eczema, How Each Is Handled and treated:
- Ringworm vs Eczema vs Psoriasis:
- Psoriasis vs Eczema vs Dermatitis:
- Eczema vs Psoriasis on the scalp:
- Eczema or Psoriasis on eyelids:
- Eczema and Psoriasis Treatment:
- Psoriasis vs Eczema, Home Remedies:
- Take-Home Message:
- FAQs:
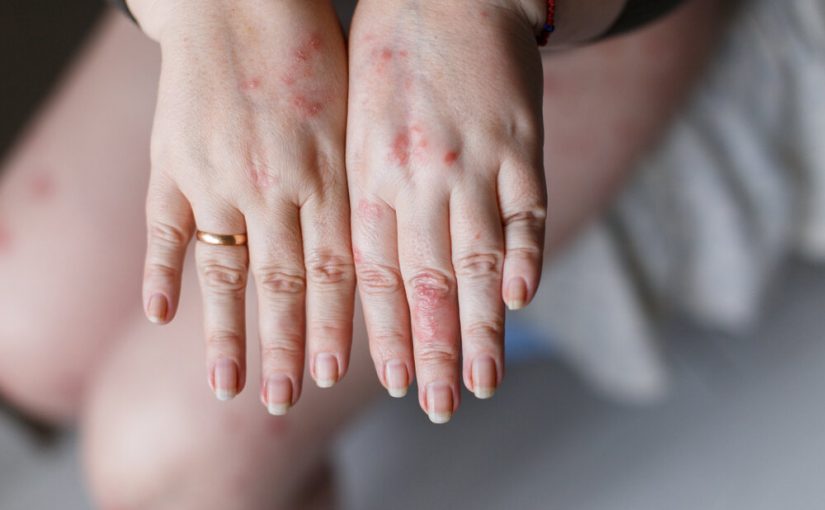
Eczema produces a severe itch. It may become so bad that you itch until your skin begins to bleed. Psoriasis may also itch, but there is a secondary condition present. Your skin could burn or hurt. Some claim that it feels like fire ants are biting you.
Skin that has eczema is irritated and red. It could be crusty, leaking, or scaly. You might notice irregular, leathery spots that are occasionally dark. Swelling may also result from it.
Red patches can also result from psoriasis. They could have elevated, scaly, and silvery skin. The skin is thicker and more irritated than it is with eczema, though, if you examine it closely.
Both Psoriasis vs Eczema on hand can be observed as areas of red, raised, itchy skin that occur. Although neither illness is communicable, both can cause infections. Although it may be difficult for the untrained eye to distinguish the distinctions, an experienced dermatologist may be able to.

Psoriasis is widespread in the United States, even though eczema can be more common. This makes self-diagnosis even more challenging because there is a significant likelihood of developing either ailment.
People frequently mix up scalp eczema vs psoriasis, but you should be aware that psoriasis causes sensitive skin patches that bleed easily when scratched and typically has a whiter scale than scalp eczema. Psoriasis and scalp eczema can occasionally coexist.
An illness of the skin known as ringworm is brought on by a fungus that is very similar to Eczema or Psoriasis. Because it can result in a circular rash (formed like a ring), which is typically red and itchy, it is known as “ringworm.” Ringworm can affect anyone. The fungus that causes this infection can reside on surfaces, clothing, bedding, towels, and other household items.
Ringworm has numerous names. The terminology used in medicine is “dermatophytosis” or “tinea.” Other names for ringworm are based on where it is found on the body; for instance, “athlete’s foot” is another name for ringworm on the feet. Now, you undertand about Psoriasis vs Eczema.
Psoriasis vs Eczema on face:
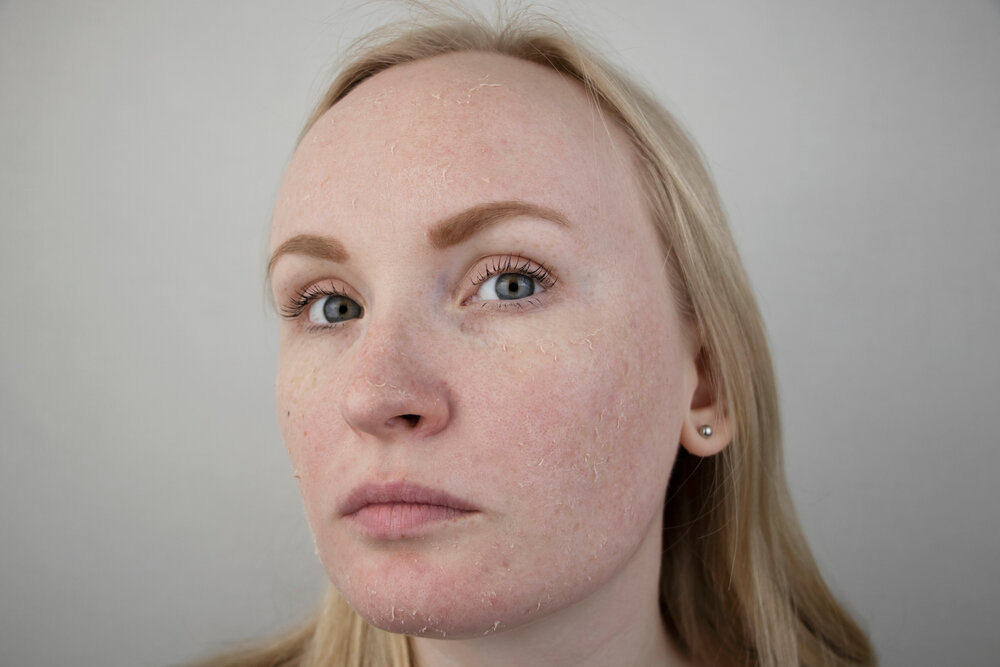

Small, red pimples that develop into red or pink ulcers on the face are typically caused by psoriasis. Frequently, silvery-white plaques that may break off cover these lesions. Typically, the hairline, upper forehead, eyebrows, and skin between the lips and nose are all affected by facial psoriasis. Psoriasis vs Eczema is important to distinguish their facial aspects.
A red, flaky, itchy rash that occurs on the face is known as facial eczema. The rash could split or develop into blisters that ooze or bleed. Although there is no known cause, some factors, such as allergies, asthma, and a family history of the condition, may raise your risk of acquiring it.
Psoriasis vs Eczema, Where they appear:
Eczema frequently develops in curved body regions, such as the inside of the elbow or the area behind the knees. It is possible to wear it on your wrists, ankles, and neck. It can occasionally appear on a baby’s chin, cheeks, scalp, chest, back, arms, and legs.
Psoriasis frequently appears in areas like yours:
- Elbows/Knees
- Face and scalp
- Lower back region
- Palm and sole
Other areas can be:
- Finger and toenails
- Borders of mouth and lips
- Eyelids and ears
- Some skin folds are also susceptible
Psoriasis vs Eczema, What are the triggering factors:
Eczema typically develops as a result of skin irritation from things like:
- Soaps, Detergents, or Disinfectants
- Meat juices
The following examples that can trigger Eczema include:
- Pets
- Pollen
- Mold
- Dandruff
- Some Foods
- Dust particles
- Eczema can be triggered by infections, stress, sweating, heat, humidity, and hormonal changes.
Some of these triggers—such as stress and infection—are also present in psoriasis. However, if your skin is damaged in any other way, as by Vaccination, Sunburn, or Scratches, Some pharmaceuticals, such as lithium, used to treat bipolar disorder, or those used to treat malaria, can also cause an outbreak of psoriasis. These are the triggering factors for Psoriasis vs Eczema.
Psoriasis vs Eczema, by what age do they begin?
Most often, newborns or young children develop eczema. Frequently, symptoms become better as a child grows older. Adults are less likely to contract it, but it is still possible. When that occurs, it’s typically a sign of another issue, such as stress, thyroid disease, or hormonal changes.
On the other hand, psoriasis typically manifests between the ages of 15 and 35. But those of other ages can also acquire it. An infant rarely develops it.
Psoriasis vs Eczema, Conditions They Are Related To:
Typically, skin that is dry and sensitive coexists with eczema. It’s possible that someone in your family also has asthma or hay fever. Other significant medical disorders have been associated with psoriasis. It increases your risk of developing diabetes, heart disease, or depression. Your doctor can suggest methods to relieve the symptoms of Psoriasis vs Eczema.
Psoriasis vs Eczema, How Each Is Handled and treated:
Treatment for eczema is based on how severe it is. You’ll use an emollient on your skin and a topical corticosteroid to reduce inflammation in mild to moderate cases. This kind of moisturizer has an oil or cream base rather than a water base, which could cause your skin to become even drier.
You might need to try an immune system suppressant like methotrexate, azathioprine, or cyclosporine if you have moderate to severe eczema. If all else fails, your physician might suggest a biological medication like Azathioprine (Imuran) or Dupilumab (Dupixent). You could also try ultraviolet light therapy, often known as phototherapy according to your doctor.
Ringworm vs Eczema vs Psoriasis:
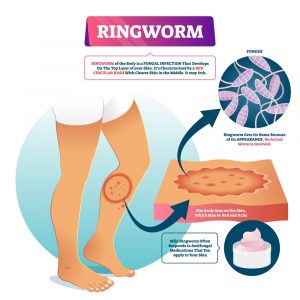
Eczema has more symptoms than ringworm does. The illness most obviously manifests as red rings on the skin. Ringworm typically only appears in a single place, whereas eczema frequently manifests as many patches. Sometimes people confuse ringworm with psoriasis, eczema, and other skin disorders. Contrary to eczema, the affected areas are always the same hue, and the patches rarely burn or even itch.
Whereas, an individual’s autoimmune conditions cause psoriasis, there are numerous ways to contract the ringworm fungus, including soil, other people, and even pets, he continues. Psoriasis results in gray or peeling, red, scaly plaques. A person experiences scaly, red, inflamed patches of skin during a psoriasis flare due to the rapid skin loss.
Moreover, a frequently scaly, red, and circular rash is brought on by ringworm. Ringworm is incredibly contagious and spreads quickly through contact with an infected person.
Psoriasis vs Eczema vs Dermatitis:
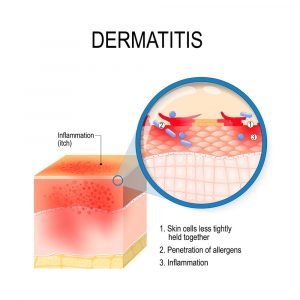
Dermatitis simply means inflammation of the skin. Whereas, Eczema is referred to as a group of skin conditions in which the skin is itchy, dry, and inflamed. The terms eczema and dermatitis are often used interchangeably. But “dermatitis” is a broader term that encompasses more than eczema rashes. Whereas, Psoriasis being a skin disease, causes rashes with itching and scaly patches.
More details are given in the next topic.
Nummular Eczema vs Psoriasis:
Nummular Eczema, also called nummular dermatitis or discoid eczema, is a persistent but curable illness that results in the development of coin-shaped lesions on the skin. These patches are usually well-defined and quite irritating. They might start to exude a clear liquid or become dry and crusty.
Although there are various reasons, nummular eczema frequently develops following a skin lesion such as a burn, abrasion, or insect bite. Coin-shaped lesions may appear in a single patch or in several patches depending on the disease. The patches may persist for a number of months.
Nummular Eczema lesions can resemble another condition brought on by psoriasis as they advance.
Additionally, itchy pimples that develop into round, itchy, scaly patches with a clear center are common symptoms of psoriasis also. On lighter skin, they may seem red or pink; on darker complexion, they may appear brown or gray. Both kinds of lesions will itch a lot. The center of the lesions usually heals first.
A dermatologist is a specialist qualified to distinguish Psoriasis vs Eczema. Between these similar-looking illnesses and other conditions with comparable appearances, such as psoriasis. Eczema causes extremely itchy skin on the neck, behind the knees, and on the inner surface of the arm.
Psoriasis frequently appears as highlighted red patches of skin covered in silvery, flaky skin. It can also affect the joints and is frequently observed on the outside of the elbows and the front of the knees.
There is another common Psoriasis condition called Plaque Psoriasis. Plaques are elevated red spots surrounded by scale, a white deposit of dead skin cells. They can appear anywhere, but they typically do on your scalp, lower back, elbows, and knees. Plaques frequently sting or irritate. It is considered an autoimmune disease.
Plaque Psoriasis vs Eczema:
When discussing your medical history with you and examining your skin, a dermatologist (skin doctor) can typically determine if you have plaque psoriasis. But identifying psoriasis can be challenging since it can resemble eczema and other skin conditions. Your doctor may occasionally need to do a biopsy. They’ll take a microscopic sample of your skin and examine the cells there. Now, you understand the context for Plaque Psoriasis vs Eczema.
Psoriasis vs Eczema vs Rosacea:
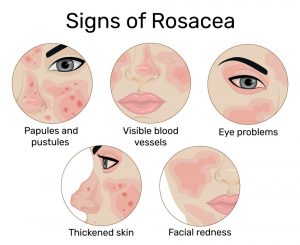
Two prevalent skin disorders with comparable symptoms are rosacea and eczema. These consist of lumps, itching, and redness. Although rosacea and eczema might be difficult to distinguish from one another, there are some significant differences.
In contrast to eczema, rosacea typically affects the cheeks and nasal bridge. It is distinguished by blushing or flushing. Rapid skin reddening followed by red spots is known as flushing.
A rosacea variant that results in fluid-filled pimples may similarly resemble an acne eruption. Small blood vessels in the middle of the face expand as a result of rosacea. Under the skin, they become visible.
Patches of eczema typically appear on certain body parts. The eyelids and skin surrounding the mouth on the face are the areas most prone to be impacted. There is no flushing or outward manifestation of blood vessels.
Psoriasis, another skin disorder, is occasionally mistaken for rosacea. An autoimmune condition is psoriasis. Silvery-white scales atop red, elevated skin patches are the main sign of psoriasis. Both psoriasis and rosacea can be triggered by genetic and aging factors, however they are two distinct diseases.
Among other symptoms, psoriasis can affect your entire body and leave red, scaly plaques on your skin. Rosacea often affects only the face, particularly the cheeks and nose, and it causes flushing. This is the common understanding for Psoriasis vs Eczema vs Rosacea.
Eczema vs Psoriasis on the scalp:
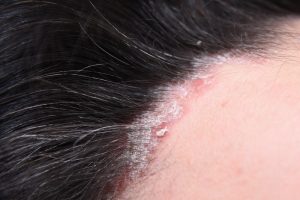
Seborrheic eczema or dermatitis and scalp psoriasis are frequent disorders that affect the scalp. They also exhibit some of the same signs and symptoms, such as red, scaly skin.
The scales of psoriasis are typically thicker and appear a little dryer than the scales of eczema. More frequently, psoriasis tends to spread past the hairline. Additionally, psoriasis typically impacts multiple body parts. If you have minor psoriasis on your elbows, knees, hands, or feet, you may also have it on your scalp. You may also notice slight nail changes, such as pitting.
Eczema or Psoriasis on eyelids:
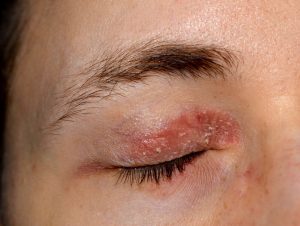
The skin on or around the eyelid can become dry, itchy, and inflamed as a result of the common condition known as eyelid dermatitis. On the eyelids, the phrase could be used to describe eczema, psoriasis, or seborrheic dermatitis. Eyelid contact dermatitis is the medical term for the ailment when an allergy or irritant is to blame. This is the common understanding for Psoriasis vs Eczema on eyelids.
Eczema and Psoriasis Treatment:

The kind and severity of Psoriasis vs Eczema affect the course of treatment. Eczema and psoriasis mild cases can be controlled with lifestyle modifications, over-the-counter medicines, and treatments.
Both skin disorders can be effectively treated with specific over-the-counter and prescription medications. However, for more severe situations, medically recommended drugs and additional treatments tailored to the individual condition will be required.
| Medication | Price | Shop |
| Imuran (Azathioprine) | $11.16 for 30 tablets | Buy Now |
| Trexall (Methotrexate) | $18.07 for 30 tablets | Buy Now |
Among the over-the-counter remedies are:
- Cortizone-10 and other topical corticosteroid creams relieve mild inflammation and discomfort.
- Symptom-relieving moisturizing lotions and ointments that reduce the likelihood of flare-ups in the future.
Prescription drugs and treatments consist of:
- Immunosuppressive medications like Imuran, Trexall, and cyclosporine stifle the body’s immunological response. They are used for moderate to severe instances of eczema and psoriasis that affect large portions of the skin.
- Different wavelengths of ultraviolet light are emitted during phototherapy, also known as light therapy, to target particular parts of the body or the entire body.
- Anthralin is frequently recommended to treat psoriasis in particular in order to limit the formation of new skin cells. The proliferation of skin cells can also be efficiently slowed down by synthetic forms of vitamin D, such as calcipotriene and calcitriol, which are frequently coupled with topical corticosteroids.
Dupilumab, an FDA-approved injectable medication, controls the inflammatory response that causes eczema flare-ups in severe cases. Tacrolimus and pimecrolimus, two topical treatments available only by prescription, also lessen eczema-related inflammation. Additionally, bacterial infections are treated with antibiotics. For Psoriasis vs Eczema treatment, much research is going on.
Psoriasis vs Eczema, Home Remedies:

Psoriasis Home remedies:
- Taking Dietary Supplements- Fish oil, Vitamin D, Aloe Vera, Oregon grape, etc.
- Prevent Dry Skin- Applying Moisturizing agents
- Trying Natural Aloe
- Avoiding Fragrances
- Soaking body with Epsom salt
- Light therapy or Phototherapy.
- Reducing stress and Alcohol intake
- Trying turmeric on flare-ups
- Quitting Smoking
Eczema Home remedies:
- Colloidal Oatmeal: Finely ground oats are used to make colloidal oatmeal. It soothes and softens irritated skin. You can get colloidal oatmeal in cream or powder form.
- Primrose Oil: Soothes irritated skin.
- Coconut Oil: natural moisturizer.
- Sunflower Oil: Topical Eczema home remedy for skin inflammation.
- Calendula cream
- Vitamin D supplements
- Tea tree oil
- Honey
- Healthy Diet
Take-Home Message:
Psoriasis vs Eczema is a frequent ailment. You could wonder if one of these disorders could be the source of skin complaints. The only way to be certain is to consult with your doctor because they can appear and feel identical.
You can work with your doctor to manage your problem once you know what it is. Whether you have eczema or psoriasis, there are several actions you may take to help, such as avoiding triggers.
While the illnesses’ origins and methods of treatment vary, the symptoms of the conditions can be similar. It is crucial to consult your doctor if you get skin symptoms like a rash, itching, pimples, or lesions. They might send you to a physician who specializes in treating skin issues.
Psoriasis vs Eczema can both be treated, but they do so in various ways. For instance, there are several drugs that are authorized to treat each ailment. Knowing your illness is still crucial, though, as some therapies, including drugs, are only appropriate for certain conditions.
FAQs:
Is Eczema and Psoriasis the same thing?
Psoriasis typically causes less intense itching and, in some rarer cases, a painful burn. On the other side, eczema can cause excruciating itching. Some people scratch their skin so vigorously that it bleeds when it becomes bad.
Eczema and Psoriasis at the same time?
Atopic eczema and psoriasis may manifest in the same person simultaneously as well as successively, according to some data. Disease coexistence may occur at a level equal to or below what is anticipated.
Is Eczema or Psoriasis contagious?
Both eczema and psoriasis can result in a rash, which are areas of red, raised, itchy skin that occur on the hands, scalp, and other parts of the body. Although neither disorder is communicable, both can result in infections.
Are Eczema and Psoriasis treated the same?
Yes, the line of treatment is somewhat in the same fashion. Psoriasis vs Eczema has comparable therapies. Among the frequent remedies are: The majority of these over-the-counter medications work to reduce symptoms or stop infections. Topical medications are there that you apply to the damaged skin as directed by your doctor. But, the oral treatment differs in both Psoriasis vs Eczema.
Can Eczema turn into Psoriasis?
Psoriasis and Eczema are two distinct diseases. No, Eczema cannot develop into Psoriasis.
Eczema or Psoriasis which is worse?
Psoriasis typically causes less intense itching and, in some rarer cases, a painful burn. On the other side, eczema can cause excruciating itching. Some individuals scratch their skin so forcefully that it bleeds when the condition becomes acute. Any of the conditions, Psoriasis vs Eczema, if left untreated, can worsen over time.