Strong Early Symptoms of Alzheimer’s Disease
The Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive disease of the brain. This destroys memory and other vital memory functions. It also leads to disturbances in the planning, reasoning, perception, and language of the patient. Alzheimer’s disease is one of the most common causes of dementia in the U.S.
The primary risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease is increased age. However, other factors like genetics also play a role in developing this disease. The possibility of having this disease increases after the age of 70, and it can affect around 50% of people over 85. Let’s Understand some Symptoms Of Alzheimer’s Disease.
Signs And Symptoms Of Alzheimer’s Disease:
- Signs And Symptoms Of Alzheimer’s Disease:
- 1. Memory Loss:
- 2. Disorientation Of Time And Place:
- 3. Difficulty In Talking Or Writing:
- 4. Struggle In Performing Known Tasks:
- 5. Vision Problems:
- 6. Poor Judgment:
- 7. Misplacing Things:
- 8. Difficulty In Planning Or Solving Problems:
- 9. Loss Of Interest In Social Work And Other Activities:
- 10. Mood Swings Or Changes In Behavior:
- Management of Alzheimer’s Disease:
- Relationship between Anxiety and Alzheimer’s Disease:
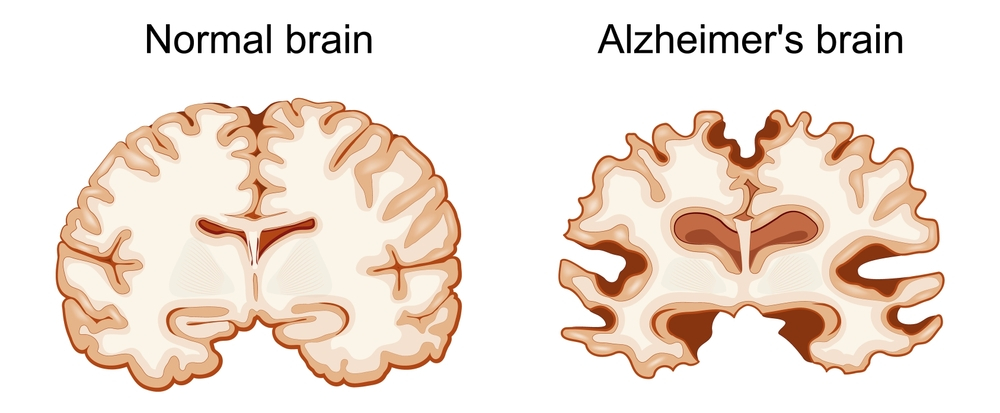
Following Are Few Signs And Symptoms Of Alzheimer’s Disease One Should Watch Out For:
1. Memory Loss:
This is often the most common early sign. Patients may forget recently learned information, important dates, or events. They may ask for the same information repeatedly and rely on memory aids like notes or electronic devices.
2. Disorientation Of Time And Place:
Patients may lose track of dates, seasons, and the passage of time. They might forget where they are or how they got there. They may also have trouble understanding something if it is not happening immediately.
3. Difficulty In Talking Or Writing:
Description: Patients might have trouble following or joining a conversation. They may stop in the middle of a conversation and have no idea how to continue or they may repeat themselves. They might struggle with vocabulary, have problems finding the right word, or call things by the wrong name.
4. Struggle In Performing Known Tasks:
There can be difficulty in completing everyday tasks at home, at work, or at leisure. For example, patients may have trouble driving to a familiar location, managing a budget, or remembering the rules of a favorite game.
5. Vision Problems:
Some people have vision problems which can be a sign of Alzheimer’s. This may include difficulty reading, judging distance, and determining color or contrast, which may cause problems with driving.
6. Poor Judgment:
Patients may experience changes in judgment or decision-making. They might use poor judgment when dealing with money, such as giving large amounts to telemarketers. They may also pay less attention to grooming or keeping themselves clean.
7. Misplacing Things:
Patients may put things in unusual places. They may lose things and be unable to go back over their steps to find them again. Sometimes, they may accuse others of stealing, especially as the disease progresses.
8. Difficulty In Planning Or Solving Problems:
Patients may experience changes in their ability to develop and follow a plan or work with numbers. They may have trouble following a familiar recipe or keeping track of monthly bills. They may have difficulty concentrating and take much longer to do things than they did before.
9. Loss Of Interest In Social Work And Other Activities:
Patients may start to withdraw from hobbies, social activities, work projects, or sports. They may have trouble keeping up with a favorite team or remembering how to complete a favorite hobby. They may also avoid being social because of the changes they have experienced.
10. Mood Swings Or Changes In Behavior:
The mood and personalities of people with Alzheimer’s can change. They can become confused, suspicious, depressed, fearful, or anxious. They may be easily upset at home, at work, with friends, or in places where they are out of their comfort zone.
Management of Alzheimer’s Disease:

There is no cure, but the disease can be managed with medication-based as well as non-medication-based treatments. The medicines can help ease the symptoms in some patients. They can aid in slowing down the development of the disease.
It is essential to talk to your doctor and figure out what options will work best for you. The doctor will assist in choosing the best treatment based on your age, medical history, and overall health. The severity of the disease is also taken into consideration.
Finally, medication or therapy that will work best for you and your lifestyle will be recommended. Furthermore, the drugs will help break down a chemical in the brain called acetylcholine, which is important for learning and memory.
The process of symptoms getting worse could be slowed down with these drugs. The effect of these drugs may last for a short time i.e. six to twelve months. Some common, mild side effects include vomiting, diarrhea, fatigue, nausea, weight loss, insomnia, and loss of appetite.
Relationship between Anxiety and Alzheimer’s Disease:
Recent research on the disease suggests a strong link between anxiety and the possibility of developing Alzheimer’s disease. The study supports the hypothesis that neuropsychiatric symptoms could represent an early onset of the disease in older adults. In the past scientists studied factors such as depression that lead to Alzheimer’s.
However, a recent study focused on specific Anxiety symptoms and concluded that it could be an early sign of the beginning of Alzheimer’s disease. Common Anxiety symptoms include fear, uneasiness, panic, insomnia, restlessness, heart palpitations, nausea, inability to set aside worry, not being about to stay calm, shortness of breath, tense muscles, etc.
In case further studies validate anxiety as an early sign of Alzheimer’s disease, it would become extremely important to identify people with Anxiety symptoms, as well as treat it effectively.
Several Anxiety drugs (Like- Prozac, Lexapro, Zoloft, Effexor, Cymbalta, etc.) are available to help people deal with this condition. Antidepressants such as escitalopram and fluoxetine work well in treating the disorder. Other than Anxiety drugs, counseling such as psychotherapy also helps in overcoming anxiety.

